
The Shift From Mobile Apps to Conversational AI
Learn More About Chatbot Fundamentals & Why It Will Increase In Importance
Introduction
…but what is Wrong with Apps?
A good point of departure is realizing the failings of apps in general. An in specific the impediments to accessing services & information. Apps present a clumsy way to organize our data in a very contained & narrow user experience. We are being forced into silos; accessing a very narrow top surface and having to drill down through functionality to access the specific service we are looking for.
There are these barriers which is baked into the nature of the app user ecosystem where we need to unlock, open, navigate, access and action.
We are being forced into these synchronous, single thread, narrow domains of rectangles and user experiences and pulled out of our multi-threaded asynchronous digital existence.

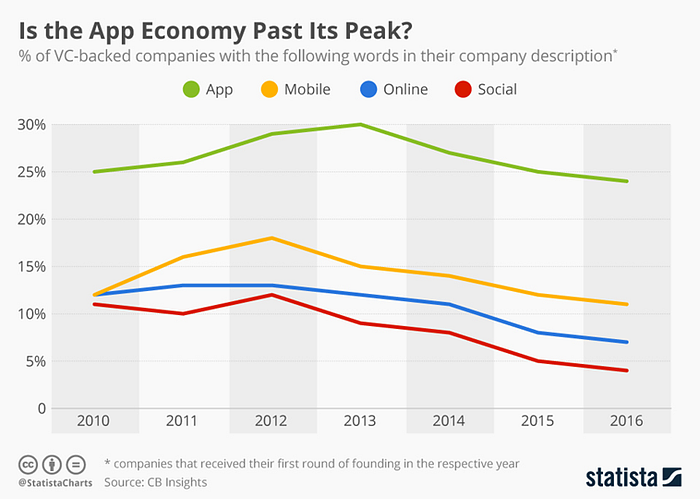
So, apps are falling out of favor with start-ups in particular. And when one modality becomes redundant, another emerges. The last 5 years we had a look at the terms in which start-up companies describe themselves, with the idea that this might give us insights into the future and give us an idea of what is the next big thing. Three terms emerged; “Virtual Reality”, “Machine Learning” and “Natural Language”; also referred to as Conversational AI.
What Apps are Actually Being Used?
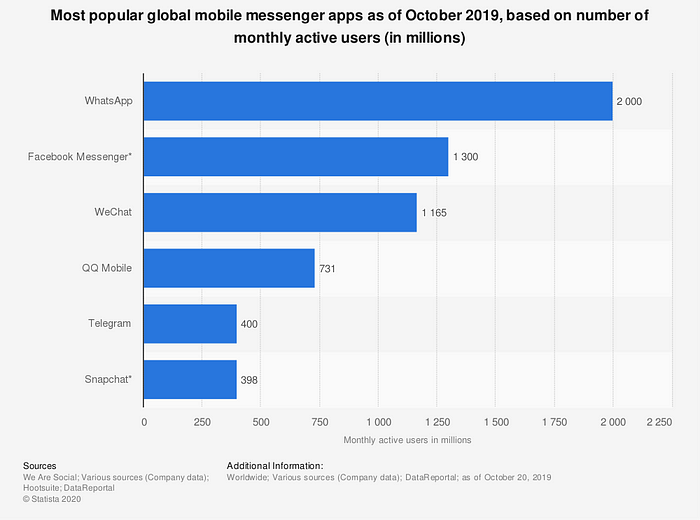
The apps we do download & use are those which suits our asynchronous multi-threaded lifestyles. Those are messaging apps. These are the apps in which we want to spend our time in.
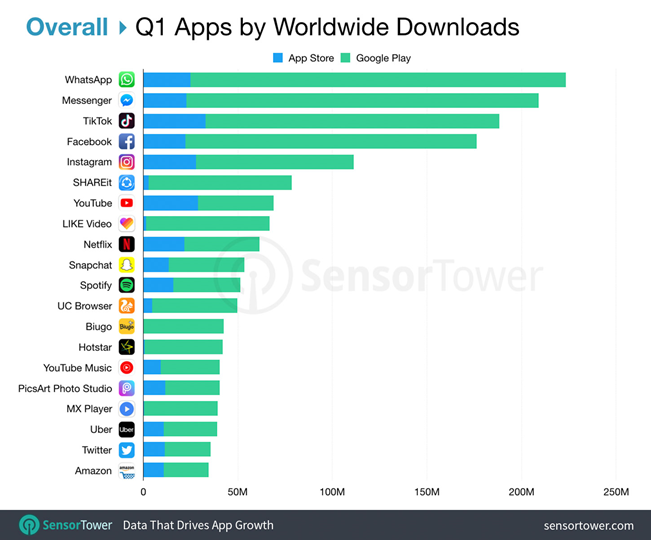
So this necessitates the notion to move our products, services and customer experience interfaces out of a declining environment, that of apps, and into these conversational, messaging environments.
And with this comes a shift in the human computer interface. For a long time there has been an extremely narrow funnel between the immense cognitive abilities of humans and the ever-expanding computational power of computers.
Going from computers to phones we lost 80% of our input capability; going from 10 to 2 fingers.
Conversation is a natural progression in the human computer interface. So we are seeing the emergence of what is called Conversational Commerce. Where services are available via our conversational platforms. And users are reacting positive to it.
The Evolution of the Human-Computer Interface

There are those who did not see the human-computer interface progressing past touch anytime soon.
Especially seeing how touch evolved and these initial loose patterns of behavior are now solidified as user convention. And these models of user convention need to be incorporated in the development of apps.
The user interface is tied to the actual and physical device. The hardware capabilities are in intricate part of the functionality available to the user.
With advances in natural language understanding and processing, we can extract language, meaning, intent and much more. We can decouple the user interface from the device’s physical capabilities. The device becomes less important and the user takes center stage. The interface adapts to the user.
But Why is Conversation so Hard…
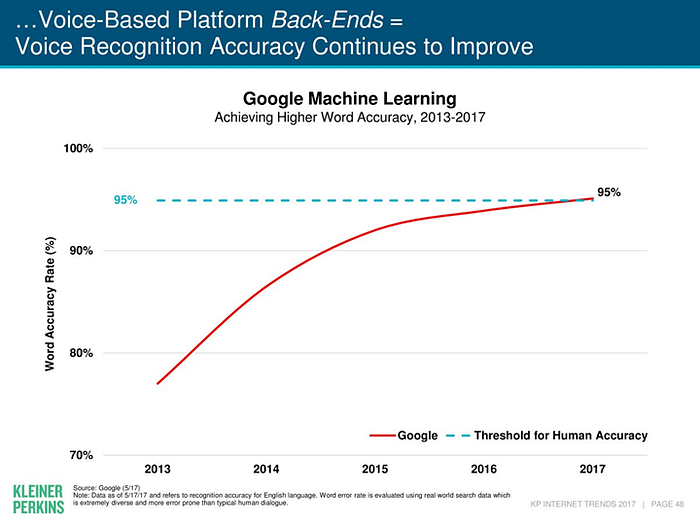
There has been huge advances in Voice recognition accuracy (ASR~Advanced Speech Recognition).
From 2017 already, computers can understand us better than what humans can. But this is only advanced speech recognition, or commonly referred to as ASR.
Taking speech and converting it to text is merely the first step.
Performing higher order Natural Language Processing (NLP) and subsequent Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is the fun part. This is where the challenge is found.
So what makes understanding language so hard?
Think of it like this…all the previous interfaces forced us to structure our data for input. Templates, forms, buttons, a graphic user interface to structure us as users. With conversation the data is highly unstructured.
The user has the freedom to structure and input conversation as they which. So the tables are turned, and the interface needs to structure the data and from there make sense of it. This is also referred to as dark data, conversations previously could be dark data. Data which could not be explored previously and from which no meaning could be extracted.
This is a brief overview of creating structure from conversation. We have found that having a higher order, first pass making use of NLP makes a big contribution, especially in the case of more complex dialogs.

Building Blocks of A Conversational AI Environment
Some elements which constitutes the NLP first pass are listed here…
Categorization
The utterance “Natural Language Understanding” will return a category of “artificial intelligence”, with a subcategory of “computer science”, and a further subcategory or science.
Entities
On a good day the process of extracting entities is hard. Establishing the location of entities using a contextual search is ideal. But in instances where the context is not clear, or there is no prior setup, general entities can be detected.
Another powerful feature is, not only to detect entities, but also detect if there are specific relation between entities. Should the user input the text “Lionel Messi won the award for the Golden Boot but no other awards were given.”, the NLU API will return the following.

A 59% certainty that an award was given to an entity identified by the type “person” and with the text “Lionel Messi”.
The words you find in a dictionary are lemmas: the base form, or root form of words.
For the most part we are still stuck with a flow which is constituted by a state machine, response scripts and in some instances the contextual transfer.
Medium Impacts Message
When it comes to chatbots, the medium impacts the message greatly. With mediums we are referring to, are for instance Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, SMS, Slack, Telegram and the like.
All of theses mediums impact the message; all these mediums have different ways in which the message can be presented.

Even though it will always be a conversation, there are conversational elements available in some mediums and not in others. You might want to look at this as components, or Conversational Components. The most basic component is Text Messages. But some mediums have the affordance of asset management, attachments, buttons, quick replies, persistent menus and more.
In Conclusion
Hence, saying the medium impacts the message. The medium determines how the message will be conveyed and received by the user.
Some mediums have a critical mass of users in some regions and not in others. This geographic consideration often determine which medium is selected for a specific region.
